In July 2023, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) announced it had opened an investigation into OpenAI, the company behind the signature artificial intelligence (AI) tool ChatGPT. According to the Civil Investigative Demand (CID) sent to OpenAI, the FTC’s investigation will address whether OpenAI engaged in:
- Unfair or deceptive privacy and security practices.
- Unfair or deceptive practices that pose a risk to consumers.
Concern over AI is part of a growing global and domestic trend of increased regulatory scrutiny of the use of AI and the risk it poses to consumers, notably consumer privacy.
More specifically, the Electronic Privacy Information Center published a “State of State AI Laws” report showing the 10 states in the last legislative year that have proposed comprehensive privacy bills, which include language to regulate AI. These proposed legislations were created to address concerns over:
- Preventing general harm to consumers.
- Protecting employees from AI.
- AI use in healthcare.
- AI use in insurance.
- Generative AI.
- AI used by government agencies.
These current events (and more) are already influencing decision-making at organizations in banking and capital markets.
Recent Examples of AI Implementation
One industry that has not been shy about investing in and implementing AI is banking and capital markets. Large banks such as Morgan Stanley, Deutsche Bank, Wells Fargo, JPMorgan Chase, and more are using AI internally and hiring AI subject matter experts at a rapid pace.
It’s estimated that the generative AI market in finance will surpass $27 billion in under 10 years, and global investment in AI technology will reach $200 billion by 2025.
Morgan Stanley recently reported using AI to launch an advanced chatbot, leveraging OpenAI’s technology to support its financial advisors in effectively utilizing the bank’s research and data library to better support their clients. Westpac decided to deploy a language model, developed on conversations and banking industry data, to support lending staff and customers for internal communications and documentation.
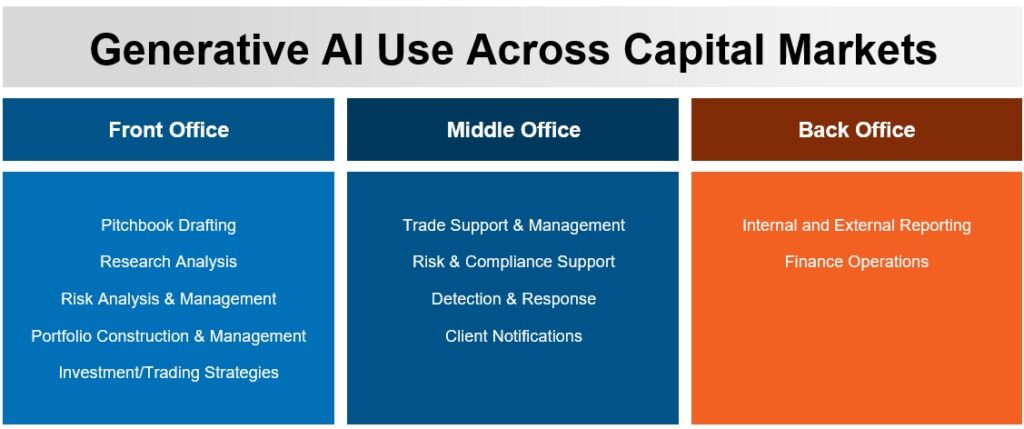
With regard to capital markets, the rising implications of generative AI are vast. Microsoft published a report that highlights the capabilities of using AI technology across front-office functions of capital markets, from leveraging content generation to build pitchbooks to generating accurate reports of research and client interactions. AI can support back-office and middle-office operations, too, through improving trade support and enhancing reporting, making AI technology an intrinsic tool across all aspects of the bank.
Below are key ways generative AI can make an impact across all operations:
AI Risks and Uncertainties Top of Mind
With several banks actively using generative AI internally and others planning to begin their implementation of AI in consumer-facing applications, banks must be mindful of proposed legislation that seeks to protect consumers from the potential harm of generative AI.
Three states (California, New York, and New Jersey), as well as the District of Columbia, have proposed legislation to protect consumers. D.C, NY, and NJ have banned or limited the use of AI for any decision-making regarding individuals using their protected personal information (such as biometric data). California and New York have proposed requiring impact assessments before the implementation of any automated decision tools.
Outside of regulation, there is an inherent risk within the technology of AI itself. Many have expressed concern about the inherent biases within AI technology.
Kim Smouter, director of the group of European Network Against Racism, noted it can be challenging knowing whether AI-based discrimination has taken place. Prominent figures in the industry, such as Rumman Chowdhury (Twitter’s/X’s former head of machine learning ethics) remarked that algorithmic discrimination already exists in financial services, particularly in lending.
Considerations for Financial Institutions to Effectively Roll-Out AI
This rising trend in regulation shouldn’t discourage financial services institutions from using AI technology effectively and ahead of regulator demands. Below are several mechanisms organizations should consider before official experimentation or adoption of AI:
Impact Assessment of AI Technology
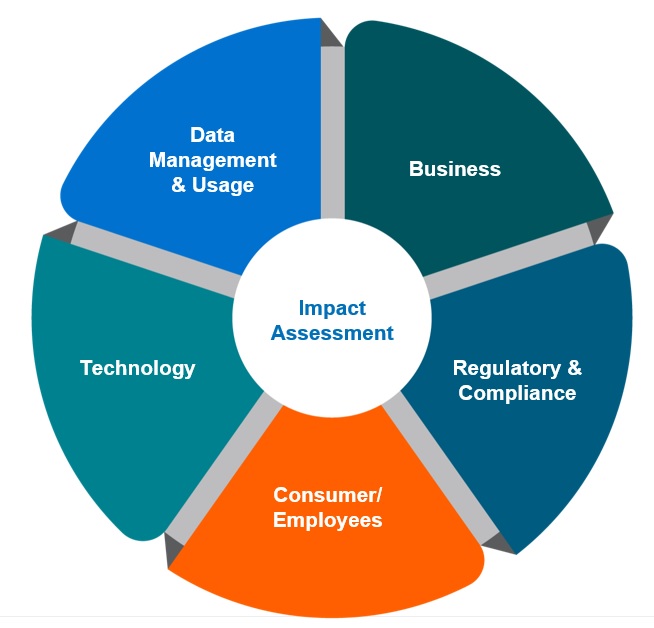
Heeding New York and California legislation, banks should conduct impact assessments on every line of business before rolling out any form of AI.
The impact assessment (visualized below) should cover technology, data, regulatory, consumer, employee, and business impacts. Apart from ensuring that the implementation of AI creates minimal risk for the bank, the impact assessment also has the benefit of documentation that enables banks to work with regulators in the future to show their due diligence and cooperation in effectively rolling out AI and protecting consumers.
Controls, Controls, and Controls
Following the completion of an impact assessment, banks can establish controls that address aforementioned AI risks as well as any other types of risk that arise as a result of the assessment. Risk leaders must ensure AI doesn’t discriminate against consumers or make use of personal information in any of its decision-making algorithms.
Controls and security measures should also extend to preventing users and bad actors from manipulating AI via its respective learning model and/or damaging the AI application by conditioning it to provide false or misleading generative content.
Governance Structure and Training
Part of effectively installing controls and implementing AI applications is effective governance. A governance structure allows banks to control and monitor how their employees use AI as well as who can train AI.
Banks and financial services institutions will also need to invest in training their employees on how to effectively use AI and how to protect the organization from AI technology at all levels.
With proper protocols in place, AI can be (and is already) an innovative tool with valuable implications and banking use cases that can’t be ignored.
Biovell ’s Banking & Capital Markets team advances key initiatives on generative AI and other progressive technologies for leading organizations amid rapid innovation. To capitalize on relevant AI opportunities at your organization with proven strategies, frameworks, and accelerators, contact Biovell .
This article is part of a series on generative AI technology, implementation strategies, use cases, and more in Banking & Capital Markets.

